Internal Sales Invoice Applet
Purpose and Overview
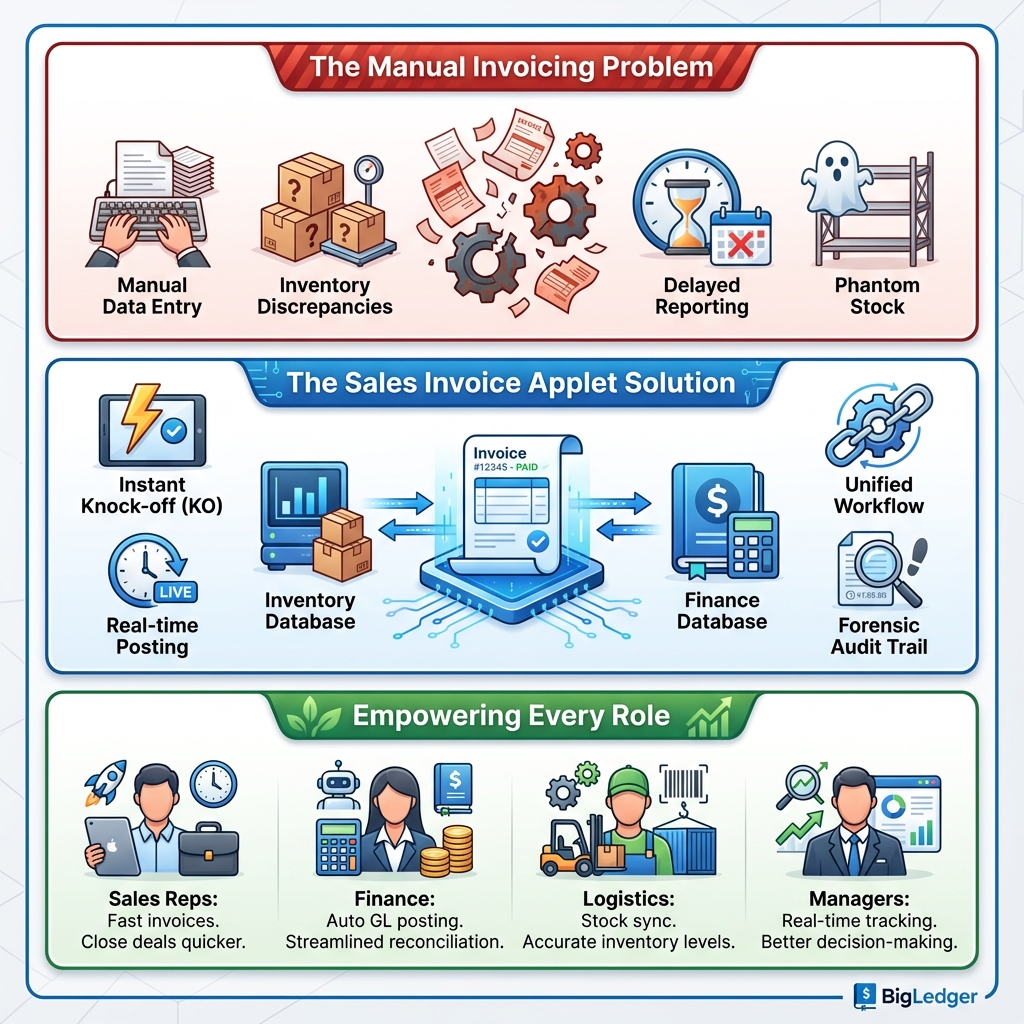
The Internal Sales Invoice Applet is the engine room of the order-to-cash process. It moves beyond simple billing by integrating sales transactions with real-time inventory deduction, financial posting, logistics coordination, and intercompany transfers.
Key Features Overview
Who Benefits from This Applet?
Sales Representatives:
- Instant Conversion: Convert confirmed orders to invoices via Knock-Off (KO) without manual re-entry.
- Strategic Efficiency: Use Templates for recurring high-volume orders.
- Inventory Visibility: See real-time stock availability to prevent over-promising.
Finance & Accounts Teams:
- Fiscal Automation: Automated General Ledger (GL) postings upon finalization.
- Intercompany Reconciliation: Seamless management of cross-entity billing.
- Compliance: Accurate tax calculations and “Selling Below Cost” alerts.
- Auditability: Complete forensic trails for every price change and status update.
Logistics & Warehouse Teams:
- Fulfillment Integration: Approved invoices automatically populate the Pick & Pack Queue.
- Correction Tools: Swap Serial allows inventory correction without financial reversals.
- Reporting: Direct link between invoicing and stock movement reports.
Business Managers:
- Control Tower: Centralized Approval Dashboard for overriding credit limits or price floors.
- Performance: Real-time sales performance monitoring.
- Security: Strict access controls via permission sets (User, Team, Role).
What Problems Does This Solve?
The Disconnected Systems Problem: Traditional sales processing often separates billing from inventory and accounting. This leads to data re-entry errors, phantom stock (selling what you don’t have), and month-end reconciliation nightmares.
The Sales Invoice Applet Solution:
- Single Source of Truth: The invoice drives the GL, Stock Card, and Logistics Queue simultaneously.
- Unified Workflow: Pack queue, delivery logistics, and intercompany transfers live in one ecosystem.
- Forensic Audit Trail: Track every click, status change, and user action.
- Flexible Settlement: Handle complex payments via Contra, Credit Notes, or Vouchers.
Key Features Overview
Key Concepts
The Invoice Lifecycle
Understanding the state transitions is crucial for effective management.
| Stage | Component | System Action | Financial Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Creation | Sales Order / Template | Confirmed demand | Reserved Stock (No GL impact) |
| 2. Billing | Sales Invoice | Finalization | Stock Deducted + Revenue Recognized + Tax Posted |
| 3. Fulfillment | Pick & Pack / DO | Goods leave warehouse | Physical stock movement verified |
| 4. Payment | Receipt/Contra | Payment received | Customer AR Balance reduced |
Intercompany Transactions
For organizations with multiple entities, this applet handles the complexity of selling from Entity A to Entity B. It automates the corresponding AP/AR entries to ensure books balance across the group, eliminating the need for manual dual-entry.
Workflow Guide
This section outlines the primary workflows for different roles, focusing on best practices and system behavior.
Efficient Invoice Generation
Goal: Create valid sales invoices that accurately reflect inventory and financial obligations.
1. Leveraging Templates & Knock-Offs Instead of manual entry, prioritize using Knock-Off (KO) from Sales Orders or Sales Invoice Templates.
- KO Logic: Inherits all customer details, pricing, and terms from the source document.
- Impact: Ensures data consistency and prevents “creative invoicing” where details differ from the approved order.
2. The Creation Form
- Entity Selection: Selecting a customer auto-populates critical financial data: Credit Terms, Default Currency, and Billing Address.
- Item Selection:
- Stock Checking: The system validates availability in real-time.
- Serialization: For serialized inventory, specific serial numbers must be allocated here to ensure the correct unit is deducted.
- Pricing: Unit prices are typically locked to the Price Book. Overrides may trigger an approval workflow.
3. Finalization & Posting Switching status to Final is the “point of no return” for financial posting.
- Immediate Actions: Revenue is recognized, Tax is posted, and Inventory is deducted.
- Logistics Trigger: The item is visible in the Pick & Pack Queue.
Management & Control
Goal: Maintain financial integrity and operational compliance.
1. Status Monitoring
- Draft: Working documents. No financial impact.
- Final: Legal documents. Locked. Requires Voiding to reverse.
- Modification: Limited editing of non-financial fields (e.g., Remarks, Delivery Instructions) on Final documents.
2. Handling Exceptions (Approvals) Sensitive actions automatically trigger the Approval Workflow.
- Triggers: Exceeding Credit Limit, Selling Below Cost, Backdating Transaction Date.
- Action: Managers review these in the Approval Permission dashboard.
- Result: The invoice remains in a “Pending” state until authorized. This prevents high-risk transactions from slipping through.
Feature Deep Dive
Sales Invoice Templates
Reduce repetitive data entry by standardizing common sales scenarios.
- Strategic Use: Create templates for “Standard Service Packs” or “Monthly Retainers”.
- Organization: Share templates with specific teams to ensure everyone sells the same package structure.
Intercompany Transactions
Manually handle complex inter-entity billing via the Intercompany route.
- Scenario: HQ purchasing bulk inventory and selling it to regional branches.
- System Logic: Accessing the Intercompany route allows you to select internal entities as customers. The system validates that the “Sales” in HQ corresponds to a potential “Purchase” in the destination entity.
Pick & Pack Queue
A dedicated view for warehouse operations to close the loop between “Sold” and “Shipped”.
- Process: Items from approved invoices appear here.
- Action: Warehouse staff mark items as “Picked” (gathered) and “Packed” (ready for courier).
- Outcome: Generates the Delivery Order (DO) and updates the shipment status, providing visibility to Sales teams.
Swap Serial
A critical tool for correcting inventory errors without financial rollback.
- The Problem: You sold “Serial A” physically, but the invoice says “Serial B”.
- The Fix: Instead of Voiding (which messes up the accounts for a non-financial error), use Swap Serial.
- Result: The system swaps the serial numbers in the backend inventory records while keeping the Invoice and GL entries intact.
Contra Settlements
Contra Settlement allows you to pay an invoice using other documents instead of cash.
- Use Case: You buy raw materials from Supplier X and sell finished goods to Customer X (same entity).
- Execution: In the Contra tab, “Knock Off” the Invoice against a Credit Note or Purchase Bill to offset the balance.
Document Tracing
The Trace button is your audit best friend.
- Financials: Review the exact Journal Entries (Debit AR / Credit Sales) generated.
- Inventory: Verify which Batch or Serial Number was deducted from which Location.
- Costing: specific Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) calculation for that transaction.
Line Reports
Configuration & Settings
Customize the interface to match your workflow.
Personalization Menu
Access the Personalization menu to adapt the applet to your specific role.
- Default Settings: Set Default Branch and Location to avoid repetitive selection.
- View Layouts: Switch between Horizontal (Data-dense) or Vertical (Visual) orientation.
Admin Configuration
System Administrators can fine-tune behavior via the Settings panel.
- Field Settings: Toggle visibility of Profit Margin, Cost Price, etc., based on user roles.
- Workflow Settings: Define custom logic for approval flows (e.g., “Invoices > $10k require Manager”).
- Printable Format Settings: Customize the Tax Invoice and Delivery Order PDF layouts with company branding.
- Webhooks: Set up event-driven notifications to external systems (e.g., “On Finalize -> Send to Slack”).